Содержание Show
Force majeure isn’t the sole justification for a Schengen visa extension. Personal reasons can also be recognized as valid grounds for extending your stay — under certain circumstances.
Find out about the grounds for extending the visa, the necessary documents for application, and the process of extension.
Grounds for extending a Schengen visa
A Schengen visa permits a stay of up to 90 days within 180 days in the Schengen Area, encompassing 27 European countries. Typically, a foreign national must exit the Area once their visa expires or they reach their stay limit. However, under special circumstances, it’s possible to apply for a visa extension.
A visa extension is only feasible if the foreigner has spent less than 90 days within the Schengen Area in the past 180 days and their current visa is still valid. If these conditions are not met, the foreigner is required to exit the Schengen Area and apply for a new visa.
Late entry. If a foreigner enters a Schengen state after their visa’s initial start date, they may be eligible for an extension. For instance, if the visa is effective from June 1st, but the foreigner enters on June 15th, they can request to prolong their visa duration accordingly.
Force majeure. According to EU law, force majeure is defined as an unforeseeable, abnormal event or circumstance that could not have been avoided, and that is beyond the control of a person referring to such an event.
A Schengen visa can be extended if force majeure occurs either in the host country or the visa holder’s home country. To obtain an extension, the visa holder must provide evidence of the force majeure event that hinders their ability to leave the country.
Examples of force majeure include:
- natural disasters, such as fires, storms, floods, earthquakes, etc;
- political or civil disturbances, such as strikes, riots, and wars;
- travel disruptions, such as cancellation of flights or sea voyages;
- other significant incidents, such as terrorist attacks and epidemics.
Humanitarian reasons. If foreign nationals encounter an unforeseen and urgent situation during their stay, they may be eligible to request a visa extension on humanitarian grounds. This need should be unexpected and not foreseeable before they enter the country.
Examples of humanitarian reasons include:
- urgent medical treatment required by the visa holder;
- significant family events involving close relatives, such as illness, childbirth, death, or marriage.
Personal reasons for extending a Schengen visa often involve professional commitments, such as a rescheduled meeting or an unforeseen conference. These circumstances may be valid grounds for a visa extension. To support their application, the visa holder must submit documentation proving the relevance and significance of the event.
How to extend a Schengen visa: step-by-step process
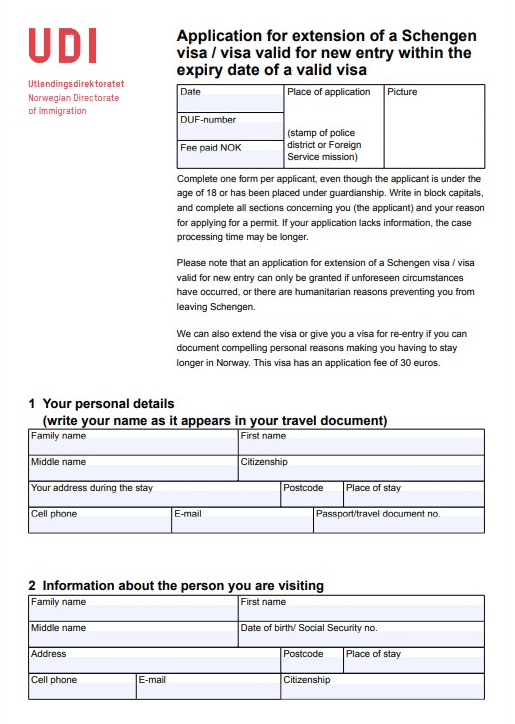
To extend a Schengen visa, a foreigner must gather the necessary documents and submit them along with an application to the local police or immigration office, depending on the specific country of stay.
-
1 dayCollecting documents
The documentation for a Schengen visa extension includes a valid passport, a recent bank statement, and valid health insurance. Additionally, the applicant must provide specific documents that substantiate the need for extending the visa.
-
1 dayApplying
To apply for a visa extension, a foreigner should submit the required documents and a completed application form and pay the applicable fee. It is advisable to apply at least 15 days before the current visa’s expiration.
The authority responsible for processing such applications varies by Schengen state. For instance, in Belgium, applications are handled by municipal administrations, while in Norway, they are managed by the local Immigration Office.
In situations of late entry, one can apply for an extension from outside the country. In such cases, the application and documents should be submitted to the respective consulate.
-
up to 1 monthProcessing the application
The responsible authorities review the application and make a decision based on the reasons provided by the applicant.
The processing time for a visa extension varies by country and can range from one day to a month. For instance, the Berlin Immigration Office in Germany has a rule to process extensions on the same day whenever feasible.
-
1 dayCollecting the passport
Once a decision is reached, the applicant must collect their passport. If the visa extension is granted, a new Schengen visa sticker will be affixed to the passport.
Documents and fees for Schengen visa extension
Documents. To extend a Schengen visa, the standard document list includes:
- Passport with a valid visa, which should be valid for at least three months beyond the intended departure date.
- A country-specific application form, typically completed online and printed.
- Travel health insurance with a minimum coverage of €30,000.
- A bank statement or other proof of sufficient funds for the extended stay.
- Documents substantiating the extension request, such as an invitation to a business meeting or a medical certificate.
Authorities may sometimes ask for extra documents or further information. For instance, in Belgium, an explanatory letter detailing the reason for the visa extension is required. In Germany, applicants might need to attend an interview for the visa extension process.
Fees. The fee for a Schengen visa extension varies based on the reason for the extension. Extensions due to force majeure or humanitarian reasons are exempt from fees.
The fee is €30 for extensions necessitated by late entry or personal reasons. This fee is payable at the time of application at the immigration office.
A second extension of a visa is also possible, provided the total duration of stay doesn’t exceed 90 days within the last 180 days post-extension. The fee for a second extension is €60 for adults and €30 for minors.
Alternatives to extending a Schengen visa
When a Schengen visa extension isn’t feasible, alternative paths can be explored.
Applying for a new Schengen visa. This approach requires the foreigner to exit the Schengen Area and apply for a new visa from outside the region.
Getting a national visa. Unlike the short-term Schengen visa, a national visa offers a longer duration of stay. It is granted for specific purposes like studying, working, or receiving medical treatment and is issued as a visa sticker in the passport. A national visa permits the holder to enter and reside in the issuing country for a period exceeding 90 days.
For instance, to obtain a national work visa, an individual from another country must secure an employment contract with a company operating within the Schengen Area. This visa is granted for 4 months. Within this timeframe, the visa holder is required to enter the employment country and submit an application for a residence permit. Typically, the residence permit is valid for one year.
The application fee for this process varies depending on the specific country, but generally, it is capped at €150.
Applying for a residence permit. A residence permit, distinct from a national visa, is typically a plastic card that functions similarly to a local ID in a Schengen country. It grants a foreigner the right to reside in the country and offers more privileges than a visa. Normally, it takes up to 8 months to get a residence permit in the Schengen area.
Eligible categories for residence permits:
- employees, freelancers, and digital nomads;
- investors or real estate purchasers;
- entrepreneurs and founders of startups;
- students, scholars, and researchers;
- spouses or other family members of a Schengen country citizen;
- patients undergoing medical treatment in European clinics;
- artists and athletes;
- volunteers;
- refugees.
Essential points on Schengen visa extension
- A Schengen visa can be extended for reasons such as late entry, force majeure, humanitarian, or personal circumstances. The visa must be valid at the time of applying for an extension.
- To apply, a foreign national gathers the required documents and submits them to the local authorities. The processing time ranges from one day to a month.
- Documents needed for extension include a passport, health insurance, bank statement, application form, and evidence justifying the extension. The standard fee for this process is €30.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, extending a Schengen visa is possible. Valid reasons for an extension include force majeure, late entry, as well as humanitarian or personal circumstances.
To extend the duration of a Schengen visa, a foreign national should collect the necessary documents and evidence supporting their need for a prolonged stay. After filling out an application form, these materials are submitted to the relevant local municipal or immigration office.
The local authorities are responsible for a visa extension. Depending on the country, it can be an immigration office, a police office, or a municipal administration. It’s advisable to consult the respective government’s website to determine the specific authority in your country of stay.
The fee for a Schengen visa extension for personal reasons is €30. However, there is no fee required for extensions due to force majeure or humanitarian reasons.
To extend a Schengen visa, the following documents are typically required:
- a valid passport;
- a completed application form;
- evidence of sufficient financial resources for an extended stay;
- valid medical insurance;
- supporting documents detailing the reasons for the extension.
Note that additional documents may be required depending on the specific country.
To extend your stay beyond 90 consecutive days in the Schengen Area, you must obtain either a long-term visa or a residence permit. This process involves determining a valid reason for the extended stay, gathering all required documentation, and formally applying for the appropriate visa or permit.
A short-term Schengen visa does not permit stays in any Schengen country for periods exceeding 90 days.
Yes, an application for a Schengen visa extension can be rejected if the authorities responsible for the decision consider the grounds for extension insufficient.
To minimise the risk of rejection, it’s important to clearly present compelling reasons for an extended stay in the Schengen Area. Commonly accepted grounds include late entry, force majeure, humanitarian or personal reasons.
To apply for a Schengen visa, a foreigner needs to fill out an application form. Schengen countries allow applicants to fill it in online via the website of a national service. However, after filling out the form online, applicants are required to visit a consulate or visa centre in person. This visit is necessary for submitting the required documents, providing biometric data, and taking a photograph.
The overall procedure remains consistent whether one is applying for a new Schengen visa or renewing an existing one.








